|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man12)
UP600-700 PR-58HA Printer Service and Parts Manual
Service Manual
|
26
|
1.2 MB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man24)
UP600-700 Parts Guide
Service Manual
|
23
|
874.46 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man23)
UP600-700 Program Manual
Service Manual
|
51
|
4.25 MB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man22)
UP600-700 Option Installation Manual
Service Manual
|
11
|
862.47 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man21)
UP600-700 Printer Manual
Service Manual
|
26
|
1.03 MB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man20)
UP600-700 Network Card Manual
Service Manual
|
20
|
2.45 MB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man19)
UP600-700 Magnetic Card Reader Manual
Service Manual
|
4
|
161.51 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man18)
UP600-700 Memory Board Manual
Service Manual
|
5
|
1.41 MB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man16)
Contactless Clerk Key Service Manual
Service Manual
|
5
|
292.25 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man15)
Circuit Diagrams manual for UP700C
Service Manual
|
15
|
343.63 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man14)
UP700C Parts Guide Manual
Service Manual
|
10
|
348.33 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man13)
Chip, PIN Concept Manual
Service Manual
|
5
|
173.23 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man11)
UP-600 700 Internal Printer PR-58HA Service Parts Manual
Service Manual
|
26
|
1.2 MB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man25)
UP600-700 Service Manual
Service Manual
|
51
|
2.63 MB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man26)
UP700 Operation Manual
User Manual / Operation Manual
|
127
|
2.55 MB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man27)
UP600 Operation Manual
User Manual / Operation Manual
|
127
|
2.7 MB
|

|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man10)
Graphic Download Utility for the UP600 700 integral printer
Service Manual / Specification
|
|
1.73 MB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man9)
Documentation on how to connect Avery A702 to UP600 UP700 including cable specification
Service Manual / Specification
|
1
|
43.16 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man60)
UP600 700 SSP-029, Report Discrepancies between PLU and System General Report
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
21.88 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man57)
SSP030 UP600 700 (Version 1A to 1G), Measures to prevent possible overheating of solenoid on cutter assembly, , , IMPORTANT
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
3
|
29.59 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man58)
SSP088 UP600 700 (Version 1A to 1G) Enables the downloading of an 02fd.exe backup created on the UP700C to be sent to a UP600 700
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
2
|
20.22 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man59)
Information regarding connection of DWL-810, for Wireless Networking
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
54.1 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man50)
APLD Cable Availability (The Sharp APLD cable is available from CPC, details contained)
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
48.79 KB
|

|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man56)
SSP030.RCV file for downloading SSP030 for use with 02FD.EXE Measures to prevent possible overheating of solenoid on cutter assembly, , IMPORTANT
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
|
30.68 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man55)
SSP031 UP600 700 (Version 1A to 1G) Disables the viewing of the Sales Total prior to the CCD report being taken on the UP600 700
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
2
|
21.5 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man54)
Modified parts for Printer Cover to prevent spillage entry.
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
4
|
365.08 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man53)
Drawer Solenoid failure UP700C., In extreme ambient temperature the Temperature Fuse within the solenoid can blow.
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
4
|
258.71 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man52)
UP600 700 SSP-029...To prevent Descrepencies between PLU Sales and General Sales Report
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
2
|
25.3 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man51)
UP700C SSP-001 PLU Sales Report descrepencies
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
24.43 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man82)
UP-700 SSP-001 (Problem assigning Direct Key 97 to keyboard)
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
6.32 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man61)
Wireless Network Solution for ER-A771, UP-600, UP-700, UP-3301
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
150.58 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man62)
SSP028 UP600 700 (Version G) Enables the LACKING MEMORY message on the Satellite when using Customer Accounts., , , VERSION G ONLY
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
2
|
20.63 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man63)
SSP026 UP600 700 (Version 1A to 1F) Enables the LACKING MEMORY message on the Satellite when using Customer Accounts., , , VERSION 1A to 1F ONLY
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
2
|
20.47 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man64)
Technical Update SSP-023 Error setting up PLU's when using over 16384 PLU's causing Screen to Disappear
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
8.49 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man65)
Unseating of RAM Board in the UP-600, UP-700, , NEW, , Spare Part PCUSS2424BHZZ
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
85.77 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man66)
Technical Bulitin to prevent the RAM Board unseating during transportation in the UP-600, UP-700.
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
112.09 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man67)
ERA5RS Transistor modification to prevent Fuse and Q1 Fault.
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
8.53 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man68)
Component failure when connecting UP600 700 to Remote Display UP-P16DP.
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
5.21 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man69)
Ordering New 02 memory boards
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
5.1 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man70)
Euro Questions
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
10.55 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man71)
SSP008 UP600 700 (Version 1B 1D), Prevents mis-calculation in System PLU Report.
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
3
|
20.51 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man81)
UP-600 700 SSP-002 (Problem X Z In-Line report not deducting ITEM, )
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
6.14 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man80)
UP600 700 Network Communication errors after power off.
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
54.87 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man79)
New Feature Update to allow GLU operation by Mag Card
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
103.56 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man78)
Cable Update(Support cables from Sharp Spare Parts)
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
33.45 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man77)
Technical Update SSP-004 Intermittent Lock out on Network system, when machine is not operated for a period of time
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
54.66 KB
|

|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man76)
Technical Update SSP005 to prevent intermittent lock out when changing mode switch position.
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
|
3.89 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man75)
Technical Update SSP005 to prevent intermittent lock out when changing Mode Switch position.
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
54.71 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man74)
Technical Update, New Clerk Key Cover with improved mechanical fixing. Part code, GCOVA7107BHSA
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
90.17 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man73)
D
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
1
|
62.72 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man72)
SSP007 UP600 700 (Version 1A), Prevents mis-calculation in System PLU Report.
Service Manual / Technical Bulletin
|
3
|
20.48 KB
|

|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man44)
ROM Image for UP-E10IN Network Card on the UP600 700 RBY1C (4MEG)
Driver / Update
|
|
134.28 KB
|

|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man32)
UP700C, , , ONLY, , , Main ROMs Version C RBM1C, RBN1C(Self extracing file, can be loaded via POSUtilityTool.exe)
Driver / Update
|
|
1.06 MB
|

|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man33)
UP600 700 Main ROMs Version I(Self extracting file, can be loaded via POSUtilityTool.exe)
Driver / Update
|
|
1.05 MB
|

|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man34)
UP700C, , , ONLY, , , Main ROMs Version A RBM1A, RBN1A(Self extracing file, can be loaded via POSUtilityTool.exe)
Driver / Update
|
|
1.03 MB
|

|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man35)
POSUtilityTool Version 3., This is the application used to download ROM images to various ECR models Version 3 supersedes all previous versions
Driver / Update
|
|
25.88 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man36)
Scanner codes and cable for MS7120 to Sharp ECR (UP600 700 610 570)
Driver / Update
|
4
|
12.04 KB
|

|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man37)
ER02FD Utility for uploading and Downloading RAM contents.
Driver / Update
|
|
117.41 KB
|

|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man38)
UP600 700 Main ROMs Version G(Self extracing file, can be loaded via POSUtilityTool.exe)
Driver / Update
|
|
1.05 MB
|

|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man39)
UP600 700 Main ROMs Version F(Self extracing file, can be loaded via POSUtilityTool.exe)
Driver / Update
|
|
1 MB
|

|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man40)
UP600 700 Main ROMs Version D (Can be loaded via PosUtilityTools.exe)
Driver / Update
|
|
1.02 MB
|

|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man41)
UP600 700 Main ROMs Version C (Can be loaded via PosUtilityTools.exe)
Driver / Update
|
|
1.01 MB
|

|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man42)
UP600 700 Version B Main ROMs, (Can be loaded via PosUtilityTool.exe)
Driver / Update
|
|
1.04 MB
|

|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man49)
Software Utility for downloading Graphic Logo to integral printer
Driver / Update
|
|
1.73 MB
|

|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man48)
Documentation for downloading Graphic Logo
Driver / Update
|
|
3.07 KB
|

|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man47)
Software Windows Utility for downloading Uploading all RAM.
Driver / Update
|
|
117.44 KB
|

|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man46)
Software Tool (PosUtilityTool.exe) for Downloading IPL (ROM Image)to UP600 700.
Driver / Update
|
|
21.55 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man45)
Documentation for Software Utilities
Driver / Update
|
6
|
316.94 KB
|

|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man43)
Main Board Version A ROM Images for UP600 700 (To be loaded via PosUtilitytool.exe
Driver / Update
|
|
1 MB
|

|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man2)
UP-700 sample keysheet in excel format
Handy Guide
|
|
11.9 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man8)
Checklist Guide for typical UP600 700 installation
Handy Guide
|
3
|
16.78 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man7)
UP600 700 Training Manual (Updated March2002)
Handy Guide
|
40
|
1.57 MB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man6)
UP600 700 Pre-Course Study Guide
Handy Guide
|
40
|
306.14 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man5)
Contactless Clerk Key Guide
Handy Guide
|
3
|
31.33 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man4)
UP-600, 700 Pos Utility Connection Guide
Handy Guide
|
1
|
18.52 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man3)
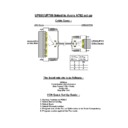
RJ45 to 9 Way, D, Type cable diagram
Handy Guide
|
1
|
14.36 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700
Metrologic MS9520 to Sharp Eprom Setup codes and cable spec
Handy Guide
|
1
|
86.15 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man31)
UP600 700 Latest FAQ's (Portrait style printer friendly) (May 2005)
FAQ
|
113
|
2.26 MB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man30)
ECR EPoS Training calendar 2005-2006
FAQ
|
1
|
27.3 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man29)
Latest FAQ's (Updated Feb 2007)
FAQ
|
114
|
349.37 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man28)
UP-600, 700 series FAQ's Updated 7th March 2012
FAQ
|
16
|
185.21 KB
|
|
|
UP-600 UP-700 (serv.man83)
Product literature
Brochure
|
2
|
407.59 KB
|