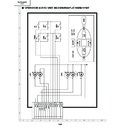
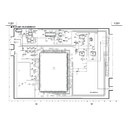
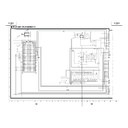
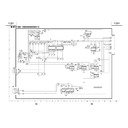
Sharp XV-Z7000 (serv.man23) User Manual / Operation Manual ▷ View online
48
Appendix
Glossary
Active digital keystone correction
Corrects keystone distortion caused when the projected image is not perpendicular to the screen. This method
provides not only horizontal correction, but vertical as well, thus maintaining the original 4:3 aspect ratio and
eliminating jag lines.
Corrects keystone distortion caused when the projected image is not perpendicular to the screen. This method
provides not only horizontal correction, but vertical as well, thus maintaining the original 4:3 aspect ratio and
eliminating jag lines.
Aspect ratio
Width and height ratio of an image. The normal aspect ratio of a computer and video image is 4 : 3. There are
also wide images with an aspect ratio of 16 : 9 and 21 : 9.
Width and height ratio of an image. The normal aspect ratio of a computer and video image is 4 : 3. There are
also wide images with an aspect ratio of 16 : 9 and 21 : 9.
Auto sync
Optimises projected computer images by automatically adjusting certain characteristics.
Optimises projected computer images by automatically adjusting certain characteristics.
Background
Initial setting image projected when no signal is being input.
Initial setting image projected when no signal is being input.
Clock
Clock adjustment is used to adjust vertical noise when clock level is incorrect.
Clock adjustment is used to adjust vertical noise when clock level is incorrect.
Colour temperature
Function that can be used to adjust the colour temperature to suit the type of image input to the projector.
Function that can be used to adjust the colour temperature to suit the type of image input to the projector.
Freeze
Function to freeze a moving image.
Function to freeze a moving image.
Gamma correction
Offers richer image viewing with dark scene phase and contrast correction according to image and room
brightness. Three gamma settings are available.
Offers richer image viewing with dark scene phase and contrast correction according to image and room
brightness. Three gamma settings are available.
GUI
Graphical User Interface. User interface with graphics that allow easier operation.
Graphical User Interface. User interface with graphics that allow easier operation.
Intelligent compression and expansion
High quality resizing of lower and higher resolution images to fit the projector’s native resolution.
High quality resizing of lower and higher resolution images to fit the projector’s native resolution.
Phase
Phase shift is a timing shift between isomorphic signals with the same resolution. When phase level is incorrect,
the projected image typically displays horizontal flicker.
Phase shift is a timing shift between isomorphic signals with the same resolution. When phase level is incorrect,
the projected image typically displays horizontal flicker.
Picture display mode
Allows you to modify or customise the picture display mode to enhance the input image.
Allows you to modify or customise the picture display mode to enhance the input image.
Progressive mode (Film mode)
Optimises the image by converting the interlaced signal to the progressive. Useful for displaying slow-moving
images or still images.
Optimises the image by converting the interlaced signal to the progressive. Useful for displaying slow-moving
images or still images.
RS-232C
Function to control the projector from the computer by using the RS-232C ports on the projector and computer.
Function to control the projector from the computer by using the RS-232C ports on the projector and computer.
Sync on green
Video signal mode of a computer which overlaps horizontal and vertical sync signal to green colour signal pin.
Video signal mode of a computer which overlaps horizontal and vertical sync signal to green colour signal pin.
Theatre mode function
Function with toggle switch to control the quantity of projected light. Select “ON” or “OFF” to decrease or
increase brightness, power consumption and fan noise.
Function with toggle switch to control the quantity of projected light. Select “ON” or “OFF” to decrease or
increase brightness, power consumption and fan noise.
48
Appendix
Glossary
Active digital keystone correction
Corrects keystone distortion caused when the projected image is not perpendicular to the screen. This method
provides not only horizontal correction, but vertical as well, thus maintaining the original 4:3 aspect ratio and
eliminating jag lines.
Corrects keystone distortion caused when the projected image is not perpendicular to the screen. This method
provides not only horizontal correction, but vertical as well, thus maintaining the original 4:3 aspect ratio and
eliminating jag lines.
Aspect ratio
Width and height ratio of an image. The normal aspect ratio of a computer and video image is 4 : 3. There are
also wide images with an aspect ratio of 16 : 9 and 21 : 9.
Width and height ratio of an image. The normal aspect ratio of a computer and video image is 4 : 3. There are
also wide images with an aspect ratio of 16 : 9 and 21 : 9.
Auto sync
Optimises projected computer images by automatically adjusting certain characteristics.
Optimises projected computer images by automatically adjusting certain characteristics.
Background
Initial setting image projected when no signal is being input.
Initial setting image projected when no signal is being input.
Clock
Clock adjustment is used to adjust vertical noise when clock level is incorrect.
Clock adjustment is used to adjust vertical noise when clock level is incorrect.
Colour temperature
Function that can be used to adjust the colour temperature to suit the type of image input to the projector.
Function that can be used to adjust the colour temperature to suit the type of image input to the projector.
Freeze
Function to freeze a moving image.
Function to freeze a moving image.
Gamma correction
Offers richer image viewing with dark scene phase and contrast correction according to image and room
brightness. Three gamma settings are available.
Offers richer image viewing with dark scene phase and contrast correction according to image and room
brightness. Three gamma settings are available.
GUI
Graphical User Interface. User interface with graphics that allow easier operation.
Graphical User Interface. User interface with graphics that allow easier operation.
Intelligent compression and expansion
High quality resizing of lower and higher resolution images to fit the projector’s native resolution.
High quality resizing of lower and higher resolution images to fit the projector’s native resolution.
Phase
Phase shift is a timing shift between isomorphic signals with the same resolution. When phase level is incorrect,
the projected image typically displays horizontal flicker.
Phase shift is a timing shift between isomorphic signals with the same resolution. When phase level is incorrect,
the projected image typically displays horizontal flicker.
Picture display mode
Allows you to modify or customise the picture display mode to enhance the input image.
Allows you to modify or customise the picture display mode to enhance the input image.
Progressive mode (Film mode)
Optimises the image by converting the interlaced signal to the progressive. Useful for displaying slow-moving
images or still images.
Optimises the image by converting the interlaced signal to the progressive. Useful for displaying slow-moving
images or still images.
RS-232C
Function to control the projector from the computer by using the RS-232C ports on the projector and computer.
Function to control the projector from the computer by using the RS-232C ports on the projector and computer.
Sync on green
Video signal mode of a computer which overlaps horizontal and vertical sync signal to green colour signal pin.
Video signal mode of a computer which overlaps horizontal and vertical sync signal to green colour signal pin.
Theatre mode function
Function with toggle switch to control the quantity of projected light. Select “ON” or “OFF” to decrease or
increase brightness, power consumption and fan noise.
Function with toggle switch to control the quantity of projected light. Select “ON” or “OFF” to decrease or
increase brightness, power consumption and fan noise.
48
Appendix
Glossary
Active digital keystone correction
Corrects keystone distortion caused when the projected image is not perpendicular to the screen. This method
provides not only horizontal correction, but vertical as well, thus maintaining the original 4:3 aspect ratio and
eliminating jag lines.
Corrects keystone distortion caused when the projected image is not perpendicular to the screen. This method
provides not only horizontal correction, but vertical as well, thus maintaining the original 4:3 aspect ratio and
eliminating jag lines.
Aspect ratio
Width and height ratio of an image. The normal aspect ratio of a computer and video image is 4 : 3. There are
also wide images with an aspect ratio of 16 : 9 and 21 : 9.
Width and height ratio of an image. The normal aspect ratio of a computer and video image is 4 : 3. There are
also wide images with an aspect ratio of 16 : 9 and 21 : 9.
Auto sync
Optimises projected computer images by automatically adjusting certain characteristics.
Optimises projected computer images by automatically adjusting certain characteristics.
Background
Initial setting image projected when no signal is being input.
Initial setting image projected when no signal is being input.
Clock
Clock adjustment is used to adjust vertical noise when clock level is incorrect.
Clock adjustment is used to adjust vertical noise when clock level is incorrect.
Colour temperature
Function that can be used to adjust the colour temperature to suit the type of image input to the projector.
Function that can be used to adjust the colour temperature to suit the type of image input to the projector.
Freeze
Function to freeze a moving image.
Function to freeze a moving image.
Gamma correction
Offers richer image viewing with dark scene phase and contrast correction according to image and room
brightness. Three gamma settings are available.
Offers richer image viewing with dark scene phase and contrast correction according to image and room
brightness. Three gamma settings are available.
GUI
Graphical User Interface. User interface with graphics that allow easier operation.
Graphical User Interface. User interface with graphics that allow easier operation.
Intelligent compression and expansion
High quality resizing of lower and higher resolution images to fit the projector’s native resolution.
High quality resizing of lower and higher resolution images to fit the projector’s native resolution.
Phase
Phase shift is a timing shift between isomorphic signals with the same resolution. When phase level is incorrect,
the projected image typically displays horizontal flicker.
Phase shift is a timing shift between isomorphic signals with the same resolution. When phase level is incorrect,
the projected image typically displays horizontal flicker.
Picture display mode
Allows you to modify or customise the picture display mode to enhance the input image.
Allows you to modify or customise the picture display mode to enhance the input image.
Progressive mode (Film mode)
Optimises the image by converting the interlaced signal to the progressive. Useful for displaying slow-moving
images or still images.
Optimises the image by converting the interlaced signal to the progressive. Useful for displaying slow-moving
images or still images.
RS-232C
Function to control the projector from the computer by using the RS-232C ports on the projector and computer.
Function to control the projector from the computer by using the RS-232C ports on the projector and computer.
Sync on green
Video signal mode of a computer which overlaps horizontal and vertical sync signal to green colour signal pin.
Video signal mode of a computer which overlaps horizontal and vertical sync signal to green colour signal pin.
Theatre mode function
Function with toggle switch to control the quantity of projected light. Select “ON” or “OFF” to decrease or
increase brightness, power consumption and fan noise.
Function with toggle switch to control the quantity of projected light. Select “ON” or “OFF” to decrease or
increase brightness, power consumption and fan noise.
48
Appendix
Glossary
Active digital keystone correction
Corrects keystone distortion caused when the projected image is not perpendicular to the screen. This method
provides not only horizontal correction, but vertical as well, thus maintaining the original 4:3 aspect ratio and
eliminating jag lines.
Corrects keystone distortion caused when the projected image is not perpendicular to the screen. This method
provides not only horizontal correction, but vertical as well, thus maintaining the original 4:3 aspect ratio and
eliminating jag lines.
Aspect ratio
Width and height ratio of an image. The normal aspect ratio of a computer and video image is 4 : 3. There are
also wide images with an aspect ratio of 16 : 9 and 21 : 9.
Width and height ratio of an image. The normal aspect ratio of a computer and video image is 4 : 3. There are
also wide images with an aspect ratio of 16 : 9 and 21 : 9.
Auto sync
Optimises projected computer images by automatically adjusting certain characteristics.
Optimises projected computer images by automatically adjusting certain characteristics.
Background
Initial setting image projected when no signal is being input.
Initial setting image projected when no signal is being input.
Clock
Clock adjustment is used to adjust vertical noise when clock level is incorrect.
Clock adjustment is used to adjust vertical noise when clock level is incorrect.
Colour temperature
Function that can be used to adjust the colour temperature to suit the type of image input to the projector.
Function that can be used to adjust the colour temperature to suit the type of image input to the projector.
Freeze
Function to freeze a moving image.
Function to freeze a moving image.
Gamma correction
Offers richer image viewing with dark scene phase and contrast correction according to image and room
brightness. Three gamma settings are available.
Offers richer image viewing with dark scene phase and contrast correction according to image and room
brightness. Three gamma settings are available.
GUI
Graphical User Interface. User interface with graphics that allow easier operation.
Graphical User Interface. User interface with graphics that allow easier operation.
Intelligent compression and expansion
High quality resizing of lower and higher resolution images to fit the projector’s native resolution.
High quality resizing of lower and higher resolution images to fit the projector’s native resolution.
Phase
Phase shift is a timing shift between isomorphic signals with the same resolution. When phase level is incorrect,
the projected image typically displays horizontal flicker.
Phase shift is a timing shift between isomorphic signals with the same resolution. When phase level is incorrect,
the projected image typically displays horizontal flicker.
Picture display mode
Allows you to modify or customise the picture display mode to enhance the input image.
Allows you to modify or customise the picture display mode to enhance the input image.
Progressive mode (Film mode)
Optimises the image by converting the interlaced signal to the progressive. Useful for displaying slow-moving
images or still images.
Optimises the image by converting the interlaced signal to the progressive. Useful for displaying slow-moving
images or still images.
RS-232C
Function to control the projector from the computer by using the RS-232C ports on the projector and computer.
Function to control the projector from the computer by using the RS-232C ports on the projector and computer.
Sync on green
Video signal mode of a computer which overlaps horizontal and vertical sync signal to green colour signal pin.
Video signal mode of a computer which overlaps horizontal and vertical sync signal to green colour signal pin.
Theatre mode function
Function with toggle switch to control the quantity of projected light. Select “ON” or “OFF” to decrease or
increase brightness, power consumption and fan noise.
Function with toggle switch to control the quantity of projected light. Select “ON” or “OFF” to decrease or
increase brightness, power consumption and fan noise.