Sharp DV-NC65H (serv.man12) Service Manual ▷ View online
18
DV-NC65H/S
DV-NC70H
DV-NC70H
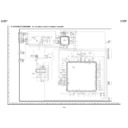
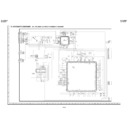
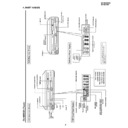
<Replacing the Pickup and the Spindle Motor>
Since the Pickup optical axis and turntable inclination of DVD are adjusted with higher accuracy, make a replacement as a
mechanism service chassis ass'y.
mechanism service chassis ass'y.
Front Side
Sled Motor Lead Wire
Pickup FFC
Traverse Fixing Screw
Loading Motor Lead Wire
Pickup Interface PWB
Pickup FFC
Short Land
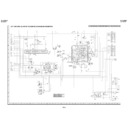
6-3. REPLACEMENT OF MAIN PARTS
<Take out disk>
1. Remove the mechanism with angle from the set. (refer to 33 on page 130. Remove K , M , N )
2. It is in such cases as the thin driver, and it is pushed in slowly, and a tray is drawn in the arrow direction the Slide Rack on the
2. It is in such cases as the thin driver, and it is pushed in slowly, and a tray is drawn in the arrow direction the Slide Rack on the
left of the base chassis.
3. Take out disk.
<Disassembling and assembling the mechanism chassis>
1. After setting the mechanism chassis to the angle state, ground it to prevent the electrostatic discharge damage of the pickup.
2. Remove the DVD Shield (lower) 40 (refer to the illustration on page 130).
3. Remove P , Q from the DVD Main PWB Unit 27 . (Pickup Relay FFC 58 isn't removed.) (refer to the illustration on page 130)
4. Remove screws fixing the base chassis (located at the back right and at front left when facing the set).
5. With the Pickup FFC connected, turn over the base chassis and short (solder) two short lands on the pickup interface PWB in
2. Remove the DVD Shield (lower) 40 (refer to the illustration on page 130).
3. Remove P , Q from the DVD Main PWB Unit 27 . (Pickup Relay FFC 58 isn't removed.) (refer to the illustration on page 130)
4. Remove screws fixing the base chassis (located at the back right and at front left when facing the set).
5. With the Pickup FFC connected, turn over the base chassis and short (solder) two short lands on the pickup interface PWB in
order to prevent the electrostatic discharge damage of the pickup.
6. Remove the Pickup FFC from the Main PWB.
7. Remove the Pickup FFC from the Pickup Interface PWB.
8. Remove the Traverse Fixing Screws to remove the Traverse Chassis ass'y.
Note: After assembling and wiring, remove the solder joint of the short land. If short-circuited, a disk is not played back.
7. Remove the Pickup FFC from the Pickup Interface PWB.
8. Remove the Traverse Fixing Screws to remove the Traverse Chassis ass'y.
Note: After assembling and wiring, remove the solder joint of the short land. If short-circuited, a disk is not played back.
19
DV-NC65H/S
DV-NC70H
DV-NC70H
7. OPERATION OF PICKUP
7-1. CIRCUIT CONFIGURATION OF PICKUP
The pickup unit reads signals from the disk, and the flexible cable is connected to the board. The following signals flow through the
cable.
cable.
7-2. EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT OF PICKUP
7-3. POLARITIES OF SIGNAL
Focus
When electric current is flowed
FO+, FO-
from FO+ to FO-, the lens comes
to near the disk.
to near the disk.
Tracking
When electric current is flowed
TR+, TR-
from TR+ to TR-, the lens goes
toward the outer circumference.
toward the outer circumference.
FO+
TR–
TR+
FO–
ACTUATOR
OSC
V
OS
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
HOLOGRAM LASER UNIT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
1
TR–
FO+
TR+
FO–
VR
PD
V
CC
GND
LD
GND
V
OS
NC
NC
V
ref
(VCC/2)
VA
VD
NC
GND
VB
VC
(NC)
Power adjust
HIGH-FREQUENCY CONVOLUTION
LD
PD
VA
VB
VC
VD
V
ref
V
cc
GND
7-4. SIGNALS OF PICKUP
7-4-1. Tracking drive signal (TR+, TR-)
The signal drives the tracking servo mechanism which projects the beam on the track by moving the objective lens (OL) to the outer
or inner circumference (at a right angle against the track) of the disk.
or inner circumference (at a right angle against the track) of the disk.
7-4-2. Focus drive signal (FO+, FO-)
The signal drives the focus servo mechanism which aligns the focus on the pit of the disk
by elevating OL (vertically against the disk surface.)
by elevating OL (vertically against the disk surface.)
The VR terminal is connected to GND.
2-focus objective lens
Actuator assembly
7-4-3. Monitor Diode (PD)
Since the laser diode largely varies output of the laser light even if the flowing current is slightly varied, the projection
light is detected with the monitor diode to control the laser light to be equally output.
Since the current varies on the monitor diode according to the intensity of the received light of the laser diode, the drive current of
the laser diode is reduced if the current of the monitor diode increases. On the contrary, the drive current of the laser diode is increased
if the current of the monitor diode decreases.
As the projection light of the laser diode becomes stronger, the current of the monitor diode increases to increase the current which
flows into the monitor diode output (PD). This is input to the pin 44 of IC301 and is compared with the reference voltage to control
the drive current of the laser diode.
The circuit is called ALPC (Automatic Laser Power Control).
light is detected with the monitor diode to control the laser light to be equally output.
Since the current varies on the monitor diode according to the intensity of the received light of the laser diode, the drive current of
the laser diode is reduced if the current of the monitor diode increases. On the contrary, the drive current of the laser diode is increased
if the current of the monitor diode decreases.
As the projection light of the laser diode becomes stronger, the current of the monitor diode increases to increase the current which
flows into the monitor diode output (PD). This is input to the pin 44 of IC301 and is compared with the reference voltage to control
the drive current of the laser diode.
The circuit is called ALPC (Automatic Laser Power Control).
7-4-4. Laser diode drive current control (LD)
Power supply to drive the laser diode
7-4-5. High-frequency convolution module power supply (VOSC)
The high-frequency convolution imposes the high-frequency signal on the DC current to impose the high frequency on the drive
current of the laser. Thus, the interference of outgoing light and reflected light is prevented.
current of the laser. Thus, the interference of outgoing light and reflected light is prevented.
LD
PD
7-4-6. HF Signal (VA, VB, VC, VD)
Signals recorded in the disk
When the quantity of laser light increases, the
current shown in figure increases and the PD
terminal voltage rises.
IC301 is used to control. The LD terminal voltage
lowers, and the quantity of light reduces. (IC301 is
actuated by voltage input.)
current shown in figure increases and the PD
terminal voltage rises.
IC301 is used to control. The LD terminal voltage
lowers, and the quantity of light reduces. (IC301 is
actuated by voltage input.)
19
DV-NC65H/S
DV-NC70H
DV-NC70H
7. OPERATION OF PICKUP
7-1. CIRCUIT CONFIGURATION OF PICKUP
The pickup unit reads signals from the disk, and the flexible cable is connected to the board. The following signals flow through the
cable.
cable.
7-2. EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT OF PICKUP
7-3. POLARITIES OF SIGNAL
Focus
When electric current is flowed
FO+, FO-
from FO+ to FO-, the lens comes
to near the disk.
to near the disk.
Tracking
When electric current is flowed
TR+, TR-
from TR+ to TR-, the lens goes
toward the outer circumference.
toward the outer circumference.
FO+
TR–
TR+
FO–
ACTUATOR
OSC
V
OS
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
HOLOGRAM LASER UNIT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
1
TR–
FO+
TR+
FO–
VR
PD
V
CC
GND
LD
GND
V
OS
NC
NC
V
ref
(VCC/2)
VA
VD
NC
GND
VB
VC
(NC)
Power adjust
HIGH-FREQUENCY CONVOLUTION
LD
PD
VA
VB
VC
VD
V
ref
V
cc
GND
7-4. SIGNALS OF PICKUP
7-4-1. Tracking drive signal (TR+, TR-)
The signal drives the tracking servo mechanism which projects the beam on the track by moving the objective lens (OL) to the outer
or inner circumference (at a right angle against the track) of the disk.
or inner circumference (at a right angle against the track) of the disk.
7-4-2. Focus drive signal (FO+, FO-)
The signal drives the focus servo mechanism which aligns the focus on the pit of the disk
by elevating OL (vertically against the disk surface.)
by elevating OL (vertically against the disk surface.)
The VR terminal is connected to GND.
2-focus objective lens
Actuator assembly
7-4-3. Monitor Diode (PD)
Since the laser diode largely varies output of the laser light even if the flowing current is slightly varied, the projection
light is detected with the monitor diode to control the laser light to be equally output.
Since the current varies on the monitor diode according to the intensity of the received light of the laser diode, the drive current of
the laser diode is reduced if the current of the monitor diode increases. On the contrary, the drive current of the laser diode is increased
if the current of the monitor diode decreases.
As the projection light of the laser diode becomes stronger, the current of the monitor diode increases to increase the current which
flows into the monitor diode output (PD). This is input to the pin 44 of IC301 and is compared with the reference voltage to control
the drive current of the laser diode.
The circuit is called ALPC (Automatic Laser Power Control).
light is detected with the monitor diode to control the laser light to be equally output.
Since the current varies on the monitor diode according to the intensity of the received light of the laser diode, the drive current of
the laser diode is reduced if the current of the monitor diode increases. On the contrary, the drive current of the laser diode is increased
if the current of the monitor diode decreases.
As the projection light of the laser diode becomes stronger, the current of the monitor diode increases to increase the current which
flows into the monitor diode output (PD). This is input to the pin 44 of IC301 and is compared with the reference voltage to control
the drive current of the laser diode.
The circuit is called ALPC (Automatic Laser Power Control).
7-4-4. Laser diode drive current control (LD)
Power supply to drive the laser diode
7-4-5. High-frequency convolution module power supply (VOSC)
The high-frequency convolution imposes the high-frequency signal on the DC current to impose the high frequency on the drive
current of the laser. Thus, the interference of outgoing light and reflected light is prevented.
current of the laser. Thus, the interference of outgoing light and reflected light is prevented.
LD
PD
7-4-6. HF Signal (VA, VB, VC, VD)
Signals recorded in the disk
When the quantity of laser light increases, the
current shown in figure increases and the PD
terminal voltage rises.
IC301 is used to control. The LD terminal voltage
lowers, and the quantity of light reduces. (IC301 is
actuated by voltage input.)
current shown in figure increases and the PD
terminal voltage rises.
IC301 is used to control. The LD terminal voltage
lowers, and the quantity of light reduces. (IC301 is
actuated by voltage input.)
19
DV-NC65H/S
DV-NC70H
DV-NC70H
7. OPERATION OF PICKUP
7-1. CIRCUIT CONFIGURATION OF PICKUP
The pickup unit reads signals from the disk, and the flexible cable is connected to the board. The following signals flow through the
cable.
cable.
7-2. EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT OF PICKUP
7-3. POLARITIES OF SIGNAL
Focus
When electric current is flowed
FO+, FO-
from FO+ to FO-, the lens comes
to near the disk.
to near the disk.
Tracking
When electric current is flowed
TR+, TR-
from TR+ to TR-, the lens goes
toward the outer circumference.
toward the outer circumference.
FO+
TR–
TR+
FO–
ACTUATOR
OSC
V
OS
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
HOLOGRAM LASER UNIT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
1
TR–
FO+
TR+
FO–
VR
PD
V
CC
GND
LD
GND
V
OS
NC
NC
V
ref
(VCC/2)
VA
VD
NC
GND
VB
VC
(NC)
Power adjust
HIGH-FREQUENCY CONVOLUTION
LD
PD
VA
VB
VC
VD
V
ref
V
cc
GND
7-4. SIGNALS OF PICKUP
7-4-1. Tracking drive signal (TR+, TR-)
The signal drives the tracking servo mechanism which projects the beam on the track by moving the objective lens (OL) to the outer
or inner circumference (at a right angle against the track) of the disk.
or inner circumference (at a right angle against the track) of the disk.
7-4-2. Focus drive signal (FO+, FO-)
The signal drives the focus servo mechanism which aligns the focus on the pit of the disk
by elevating OL (vertically against the disk surface.)
by elevating OL (vertically against the disk surface.)
The VR terminal is connected to GND.
2-focus objective lens
Actuator assembly
7-4-3. Monitor Diode (PD)
Since the laser diode largely varies output of the laser light even if the flowing current is slightly varied, the projection
light is detected with the monitor diode to control the laser light to be equally output.
Since the current varies on the monitor diode according to the intensity of the received light of the laser diode, the drive current of
the laser diode is reduced if the current of the monitor diode increases. On the contrary, the drive current of the laser diode is increased
if the current of the monitor diode decreases.
As the projection light of the laser diode becomes stronger, the current of the monitor diode increases to increase the current which
flows into the monitor diode output (PD). This is input to the pin 44 of IC301 and is compared with the reference voltage to control
the drive current of the laser diode.
The circuit is called ALPC (Automatic Laser Power Control).
light is detected with the monitor diode to control the laser light to be equally output.
Since the current varies on the monitor diode according to the intensity of the received light of the laser diode, the drive current of
the laser diode is reduced if the current of the monitor diode increases. On the contrary, the drive current of the laser diode is increased
if the current of the monitor diode decreases.
As the projection light of the laser diode becomes stronger, the current of the monitor diode increases to increase the current which
flows into the monitor diode output (PD). This is input to the pin 44 of IC301 and is compared with the reference voltage to control
the drive current of the laser diode.
The circuit is called ALPC (Automatic Laser Power Control).
7-4-4. Laser diode drive current control (LD)
Power supply to drive the laser diode
7-4-5. High-frequency convolution module power supply (VOSC)
The high-frequency convolution imposes the high-frequency signal on the DC current to impose the high frequency on the drive
current of the laser. Thus, the interference of outgoing light and reflected light is prevented.
current of the laser. Thus, the interference of outgoing light and reflected light is prevented.
LD
PD
7-4-6. HF Signal (VA, VB, VC, VD)
Signals recorded in the disk
When the quantity of laser light increases, the
current shown in figure increases and the PD
terminal voltage rises.
IC301 is used to control. The LD terminal voltage
lowers, and the quantity of light reduces. (IC301 is
actuated by voltage input.)
current shown in figure increases and the PD
terminal voltage rises.
IC301 is used to control. The LD terminal voltage
lowers, and the quantity of light reduces. (IC301 is
actuated by voltage input.)
Display